Benchmarks
View scores and output across OCR models spanning many document categories.
Want to run these evals on your own documents?
Talk to Sales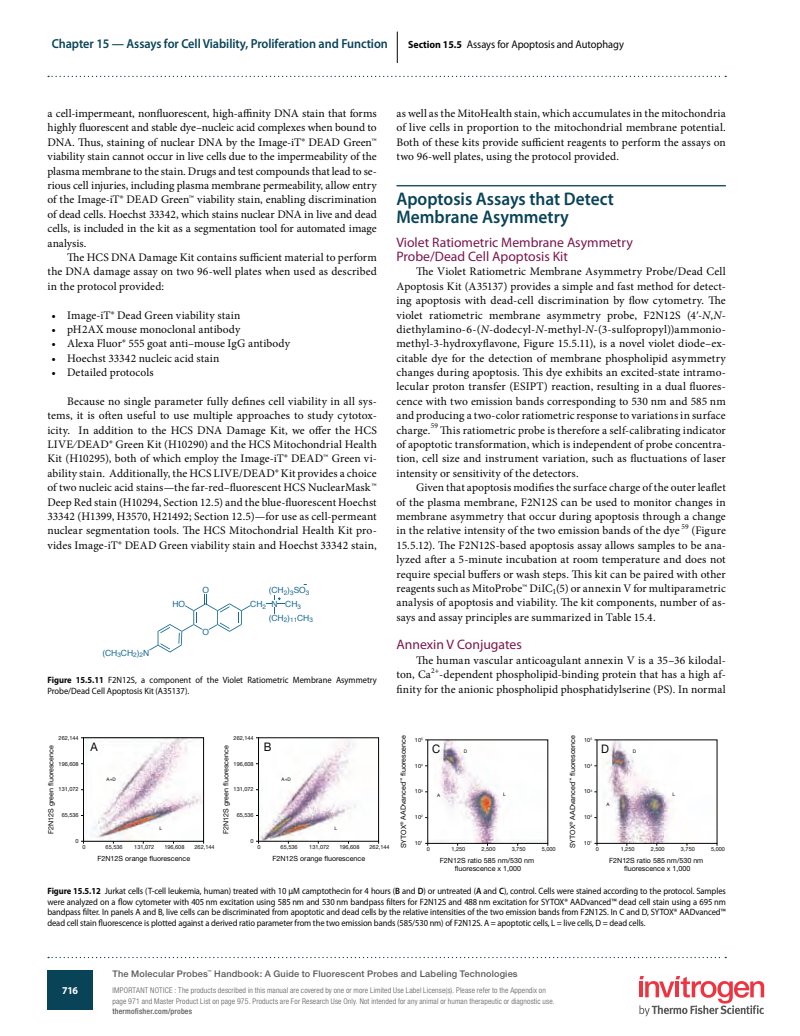
Chapter 15 — Assays for Cell Viability, Proliferation and Function
Section 15.5 Assays for Apoptosis and Autophagy
a cell-impermeant, nonfluorescent, high-affinity DNA stain that forms highly fluorescent and stable dye-nucleic acid complexes when bound to DNA. Thus, staining of nuclear DNA by the Image-iT DEAD Green viability stain cannot occur in live cells due to the impermeability of the plasma membrane to the stain. Drugs and test compounds that lead to serious cell injuries, including plasma membrane permeability, allow entry of the Image-iT DEAD Green viability stain, enabling discrimination of dead cells. Hoechst 33342, which stains nuclear DNA in live and dead cells, is included in the kit as a segmentation tool for automated image analysis.
The HCS DNA Damage Kit contains sufficient material to perform the DNA damage assay on two 96-well plates when used as described in the protocol provided:
- Image-iT Dead Green viability stain
- pH2AX mouse monoclonal antibody
- Alexa Fluor 555 goat anti-mouse IgG antibody
- Hoechst 33342 nucleic acid stain
- Detailed protocols
Because no single parameter fully defines cell viability in all systems, it is often useful to use multiple approaches to study cytotoxicity. In addition to the HCS DNA Damage Kit, we offer the HCS LIVE/DEAD Green Kit (H10290) and the HCS Mitochondrial Health Kit (H10295), both of which employ the Image-iT DEAD Green viability stain. Additionally, the HCS LIVE/DEAD Kit provides a choice of two nucleic acid stains—the far-red-fluorescent HCS NuclearMask Deep Red stain (H10294, Section 12.5) and the blue-fluorescent Hoechst 33342 (H1399, H3570, H21492; Section 12.5)—for use as cell-permeant nuclear segmentation tools. The HCS Mitochondrial Health Kit provides Image-iT DEAD Green viability stain and Hoechst 33342 stain,
as well as the MitoHealth stain, which accumulates in the mitochondria of live cells in proportion to the mitochondrial membrane potential. Both of these kits provide sufficient reagents to perform the assays on two 96-well plates, using the protocol provided.
Apoptosis Assays that Detect Membrane Asymmetry
Violet Ratiometric Membrane Asymmetry Probe/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit
The Violet Ratiometric Membrane Asymmetry Probe/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit (A35137) provides a simple and fast method for detecting apoptosis with dead-cell discrimination by flow cytometry. The violet ratiometric membrane asymmetry probe, F2N12S (4'-N,N-diethylamino-6-(N-dodecyl-N-methyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl))ammonio-methyl-3-hydroxyflavone, Figure 15.5.11), is a novel violet diode-excitable dye for the detection of membrane phospholipid asymmetry changes during apoptosis. This dye exhibits an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) reaction, resulting in a dual fluorescence with two emission bands corresponding to 530 nm and 585 nm and producing a two-color ratiometric response to variations in surface charge. This ratiometric probe is therefore a self-calibrating indicator of apoptotic transformation, which is independent of probe concentration, cell size and instrument variation, such as fluctuations of laser intensity or sensitivity of the detectors.
Given that apoptosis modifies the surface charge of the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, F2N12S can be used to monitor changes in membrane asymmetry that occur during apoptosis through a change in the relative intensity of the two emission bands of the dye (Figure 15.5.12). The F2N12S-based apoptosis assay allows samples to be analyzed after a 5-minute incubation at room temperature and does not require special buffers or wash steps. This kit can be paired with other reagents such as MitoProbe DiIC (5) or annexin V for multiparametric analysis of apoptosis and viability. The kit components, number of assays and assay principles are summarized in Table 15.4.
Annexin V Conjugates
The human vascular anticoagulant annexin V is a 35–36 kilodalton, Ca -dependent phospholipid-binding protein that has a high affinity for the anionic phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS). In normal
Figure 15.5.11 F2N12S, a component of the Violet Ratiometric Membrane Asymmetry Probe/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit (A35137).
Figure 15.5.12 Jurkat cells (T-cell leukemia, human) treated with 10 M camptothecin for 4 hours (B and D) or untreated (A and C), control. Cells were stained according to the protocol. Samples were analyzed on a flow cytometer with 405 nm excitation using 585 nm and 530 nm bandpass filters for F2N12S and 488 nm excitation for SYTOX AADvanced dead cell stain using a 695 nm bandpass filter. In panels A and B, live cells can be discriminated from apoptotic and dead cells by the relative intensities of the two emission bands from F2N12S. In C and D, SYTOX AADvanced dead cell stain fluorescence is plotted against a derived ratio parameter from the two emission bands (585/530 nm) of F2N12S. A = apoptotic cells, L = live cells, D = dead cells.
716
The Molecular Probes Handbook: A Guide to Fluorescent Probes and Labeling Technologies
IMPORTANT NOTICE: The products described in this manual are covered by one or more Limited Use Label License(s). Please refer to the Appendix on page 971 and Master Product List on page 975. Products are For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use.
thermofisher.com/probes
invitrogen
by Thermo Fisher Scientific