Benchmarks
View scores and output across OCR models spanning many document categories.
Want to run these evals on your own documents?
Talk to Sales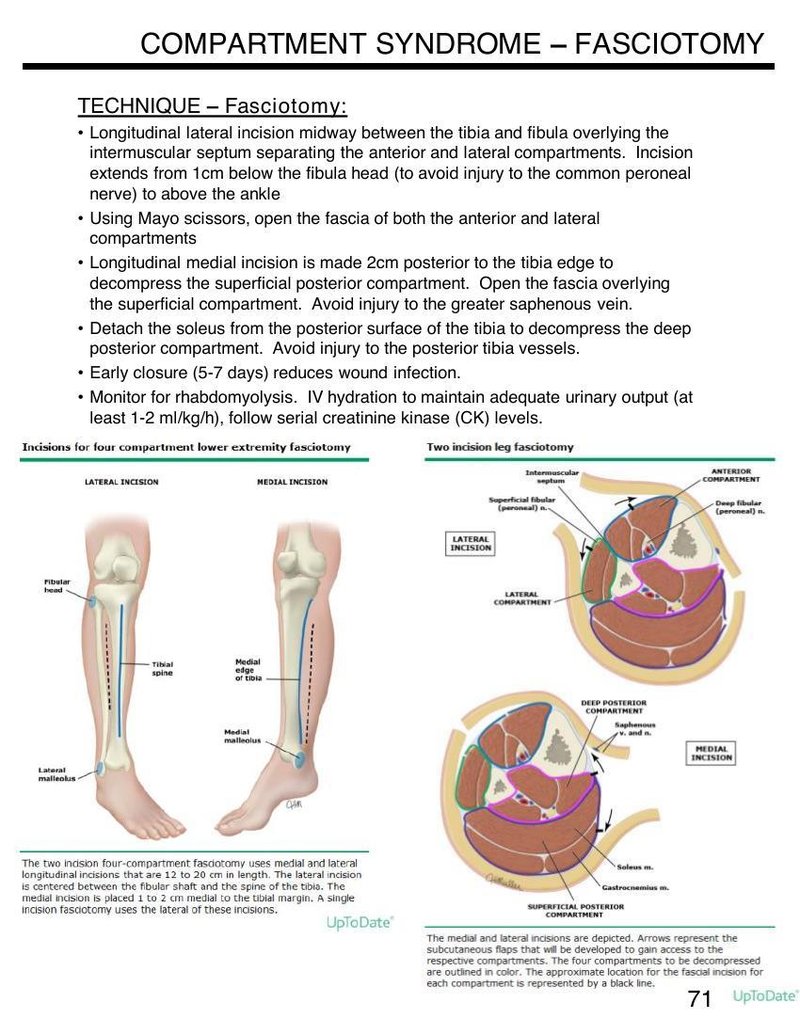
COMPARTMENT SYNDROME – FASCIOTOMY
TECHNIQUE – Fasciotomy:
- Longitudinal lateral incision midway between the tibia and fibula overlying the intermuscular septum separating the anterior and lateral compartments. Incision extends from 1 cm below the fibula head (to avoid injury to the common peroneal nerve) to above the ankle
- Using Mayo scissors, open the fascia of both the anterior and lateral compartments
- Longitudinal medial incision is made 2 cm posterior to the tibia edge to decompress the superficial posterior compartment. Open the fascia overlying the superficial compartment. Avoid injury to the greater saphenous vein.
- Detach the soleus from the posterior surface of the tibia to decompress the deep posterior compartment. Avoid injury to the posterior tibia vessels.
- Early closure (5-7 days) reduces wound infection.
- Monitor for rhabdomyolysis. IV hydration to maintain adequate urinary output (at least 1-2 ml/kg/h), follow serial creatinine kinase (CK) levels.
Incisions for four compartment lower extremity fasciotomy
The two incision four-compartment fasciotomy uses medial and lateral longitudinal incisions that are 12 to 20 cm in length. The lateral incision is centered between the fibular shaft and the spine of the tibia. The medial incision is placed 1 to 2 cm medial to the tibial margin. A single incision fasciotomy uses the lateral of these incisions.
Two incision leg fasciotomy
The medial and lateral incisions are depicted. Arrows represent the subcutaneous flaps that will be developed to gain access to the respective compartments. The four compartments to be decompressed are outlined in color. The approximate location for the fascial incision for each compartment is represented by a black line.
UpToDate®
71
UpToDate®