Benchmarks
View scores and output across OCR models spanning many document categories.
Want to run these evals on your own documents?
Talk to Sales Page 1 of 1
专题 41 有关圆幂定理型压轴题
【方法点拨】
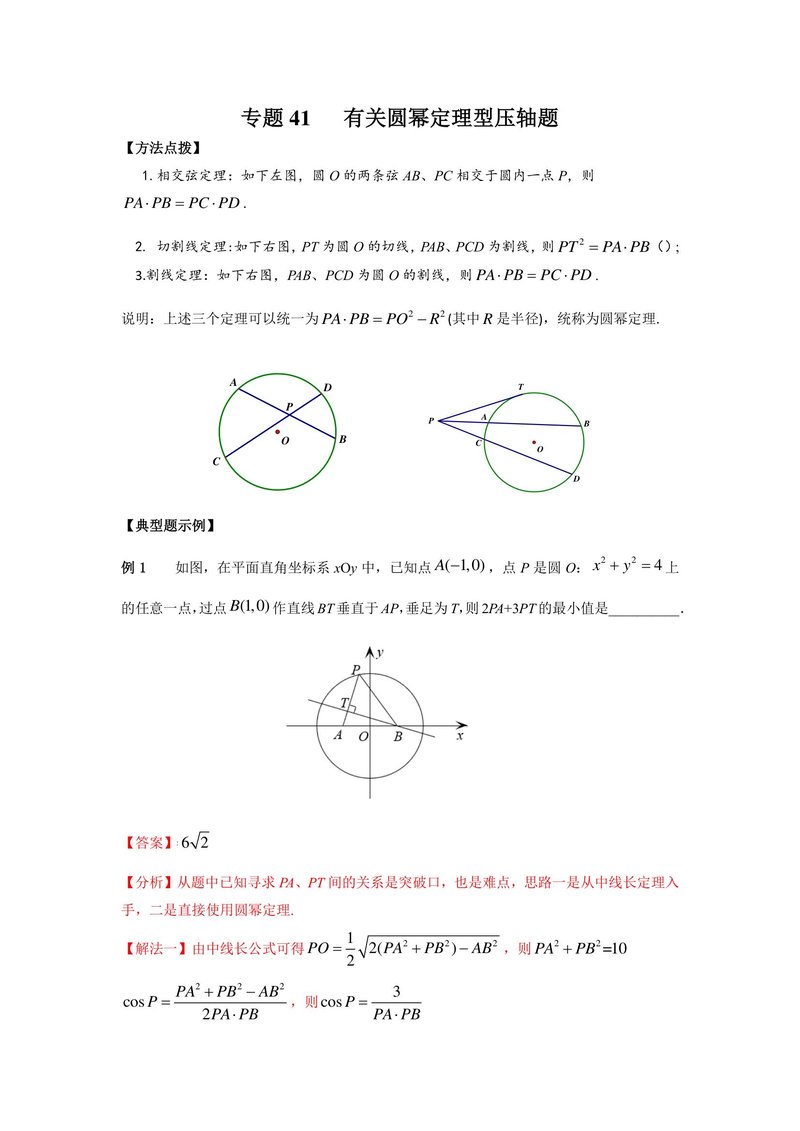
1. 相交弦定理: 如下左图, 圆 的两条弦 、 相交于圆内一点 , 则 .
2. 切割线定理: 如下右图, 为圆 的切线, 、 为割线, 则 ( ) ;
3. 割线定理: 如下右图, 、 为圆 的割线, 则 .
说明: 上述三个定理可以统一为 (其中 是半径), 统称为圆幂定理.
Diagram illustrating the Power of a Point theorem. The left diagram shows a circle centered at O with two chords AB and CD intersecting at P inside the circle. The right diagram shows a circle centered at O with a point P outside the circle, a tangent PT at T, and two secants PAB and PCD.
【典型题示例】
例 1 如图, 在平面直角坐标系 中, 已知点 , 点 是圆 上的任意一点, 过点 作直线 垂直于 , 垂足为 , 则 的最小值是________.
Diagram for Example 1. A circle centered at O (origin) with radius 2. Points A(-1, 0) and B(1, 0) are on the x-axis. P is a point on the circle. T is the foot of the perpendicular from B to the line AP, forming a right angle at T.
【答案】:
【分析】从题中已知寻求 、 间的关系是突破口, 也是难点, 思路一是从中线长定理入手, 二是直接使用圆幂定理.
【解法一】由中线长公式可得 , 则