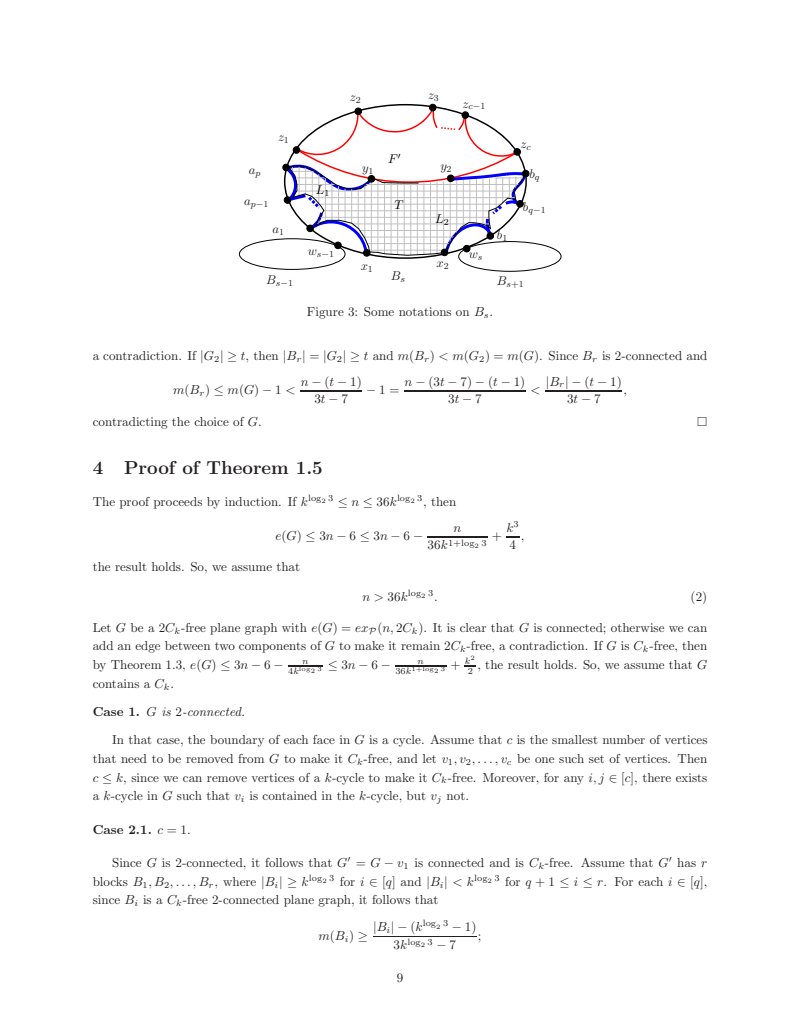
Figure 3 shows a graph structure centered around a block B_s. The boundary of B_s is a cycle containing vertices a_1, w_{s-1}, x_1, x_2, w_s, b_1, b_{q-1}, b_q, and z_c. Inside B_s, there is a region T. Two paths, L_1 and L_2, connect the boundary. L_1 connects a_1 to w_{s-1} and x_1. L_2 connects b_1 to b_{q-1} and x_2. The region T is bounded by L_1, L_2, and a path F' connecting y_1 and y_2. The path F' is shown in red, and L_1 and L_2 are shown in blue. The vertices z_1, z_2, z_3, \dots, z_{c-1} are also marked on the boundary of B_s.
Figure 3: Some notations on
.
a contradiction. If
, then
and
m(B_r)\le m(G)-1<\frac{n-(t-1)}{3t-7}-1=\frac{n-(3t-7)-(t-1)}{3t-7}<\frac{|B_r|-(t-1)}{3t-7},
contradicting the choice of
G
. □
4 Proof of Theorem 1.5
The proof proceeds by induction. If
k^{\log_2 3}\le n\le 36k^{\log_2 3}
, then
e(G)\le 3n-6\le 3n-6-\frac{n}{36k^{1+\log_2 3}}+\frac{k^3}{4},
the result holds. So, we assume that
n>36k^{\log_2 3}.
(2)
Let
G
be a
2C_k
-free plane graph with
e(G)=\operatorname{ex}_P(n, 2C_k)
. It is clear that
G
is connected; otherwise we can add an edge between two components of
G
to make it remain
2C_k
-free, a contradiction. If
G
is
C_k
-free, then by Theorem 1.3,
e(G)\le 3n-6-\frac{n}{4k^{\log_2 3}}\le 3n-6-\frac{n}{36k^{1+\log_2 3}}+\frac{k^2}{2}
, the result holds. So, we assume that
G
contains a
C_k
.
Case 1.
G
is 2-connected.
In that case, the boundary of each face in
G
is a cycle. Assume that
c
is the smallest number of vertices that need to be removed from
G
to make it
C_k
-free, and let
v_1, v_2, \dots, v_c
be one such set of vertices. Then
c\le k
, since we can remove vertices of a
k
-cycle to make it
C_k
-free. Moreover, for any
i, j\in[c]
, there exists a
k
-cycle in
G
such that
v_i
is contained in the
k
-cycle, but
v_j
not.
Case 2.1.
c=1
.
Since
G
is 2-connected, it follows that
G'=G-v_1
is connected and is
C_k
-free. Assume that
G'
has
r
blocks
B_1, B_2, \dots, B_r
, where
|B_i|\ge k^{\log_2 3}
for
i\in[q]
and
|B_i|
for
q+1\le i\le r
. For each
i\in[q]
, since
B_i
is a
C_k
-free 2-connected plane graph, it follows that
m(B_i)\ge\frac{|B_i|-(k^{\log_2 3}-1)}{3k^{\log_2 3}-7};
9